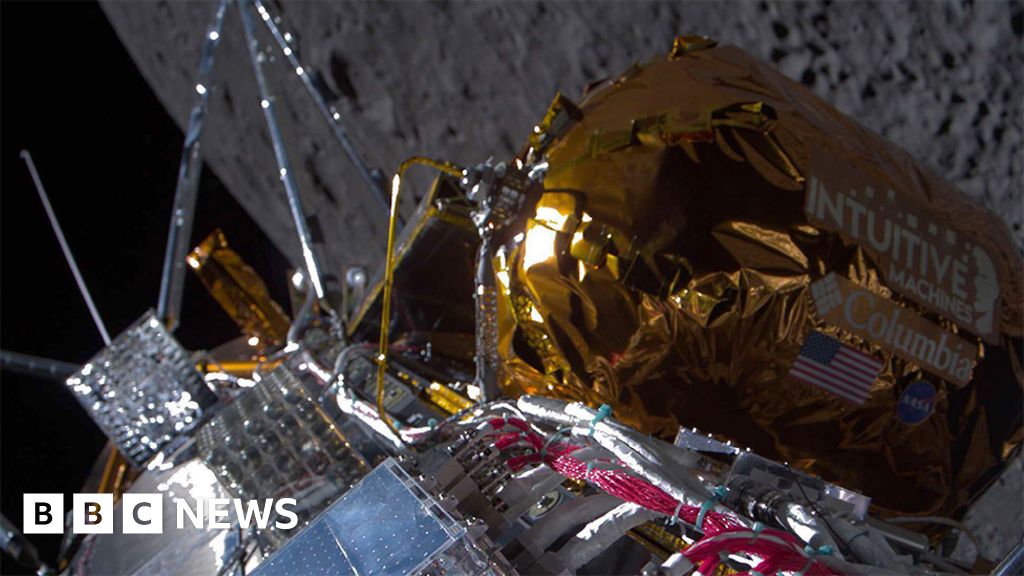
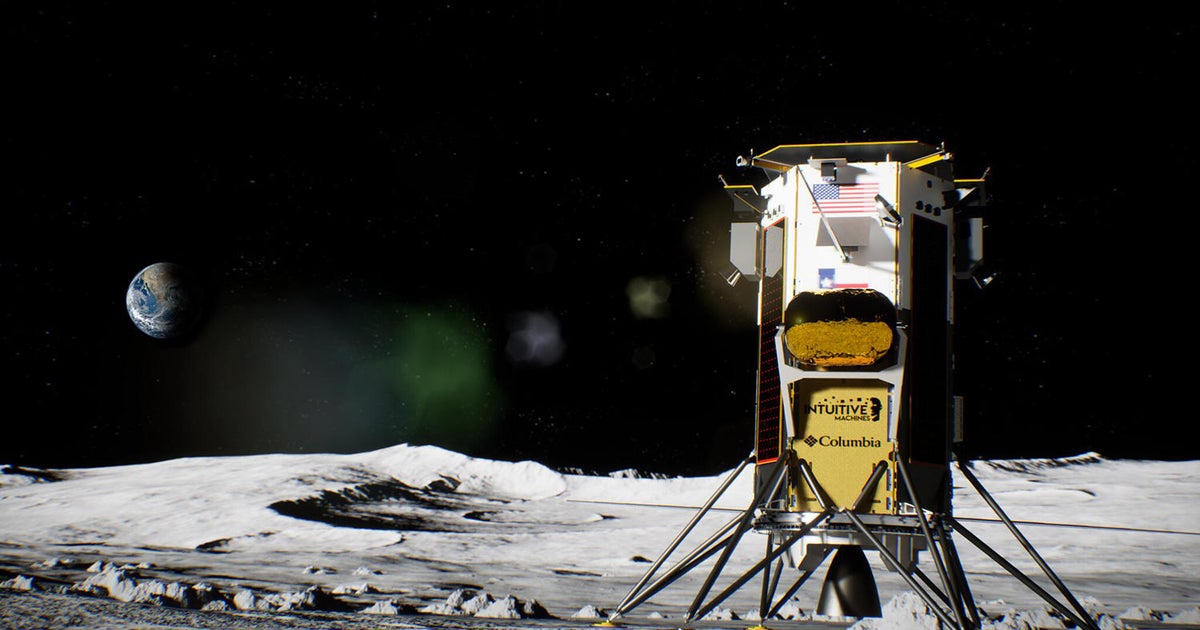
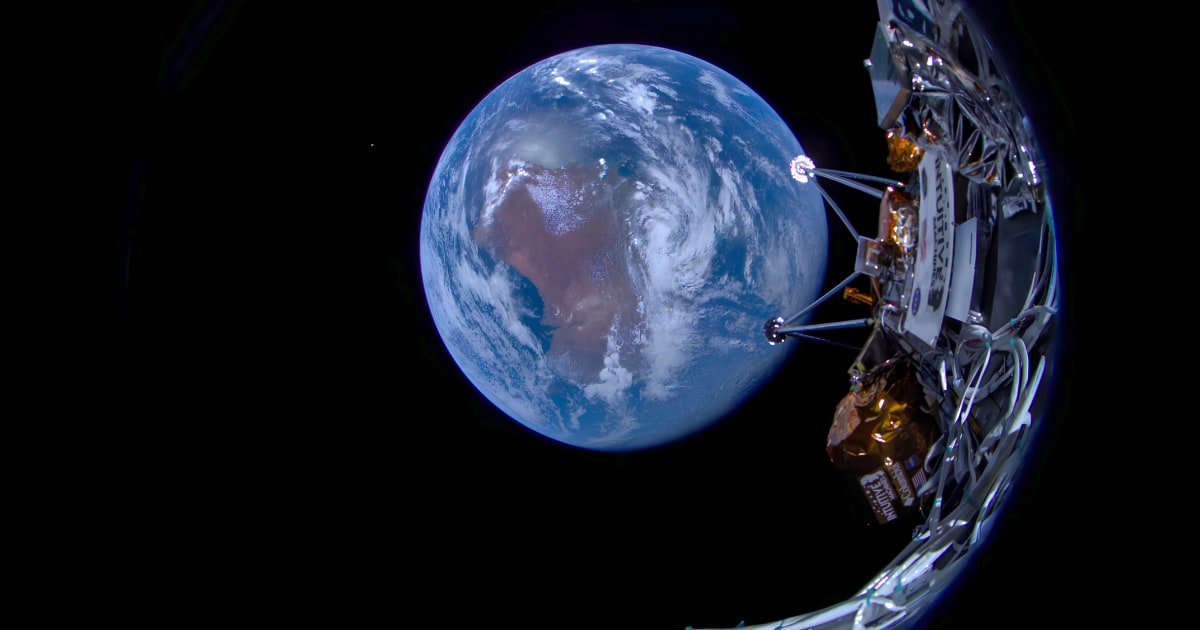
The United States has successful landed the spacecraft Odysseus on the surface of the moon. This achievement marks the first U.S. spacecraft to perform a controlled descent to the lunar soil since the Apollo 17 mission in 1972.
Also Read: Neuralink’s First Human Patient able to Control Mouse through Thinking
What sets Odysseus apart is its importance in bridging a gap of over half a century in American lunar exploration but also its distinction as the effort of a private company in landing on the lunar surface.
Launched on February 15 atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Odysseus, developed by the Texas-based company Intuitive Machines, a journey that culminated in its historic touchdown near the moon’s south pole.
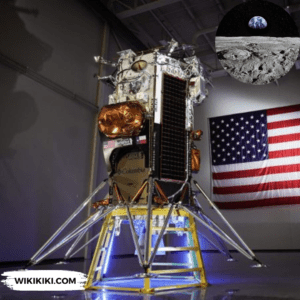
Odysseus, a six-legged robot lander standing at approximately 4 meters tall and 1.5 meters wide, carried a suite of scientific instruments and technology demonstrations onboard.
Among these payloads were six NASA instruments planned at demonstrating equipment for future lunar landings and advancing our understanding of the lunar environment. Several payloads from private companies and groups were also part of Odysseus’s cargo.
Engineers faced unexpected hurdles during the descent, including a malfunction in the spacecraft’s autonomous navigation system.
However, quick thinking and decisive action allowed mission planners to overcome these obstacles, ensuring a successful touchdown on the lunar surface.
Initial communication difficulties, flight controllers eventually confirmed that Odysseus was upright and transmitting data, marking the culmination of years of hard work and dedication.
The landing site chosen for Odysseus, near the Malapert A crater, holds importance for future lunar exploration efforts.
Situated approximately 300 kilometers from the moon’s south pole, this location offers valuable insights into the lunar environment.
Also Read: Intuitive Machines Launches First Private US Moon Lander
The chosen landing site, Malapert A, situated within an impact crater approximately 300 kilometers away from the lunar south pole, was selected by NASA for its importance in advancing our understanding of the lunar environment.
With the intention of establishing an astronaut base at the lunar south pole, NASA’s decision underlines the importance of gathering critical data to enhance communication protocols and inform future lunar missions.
Upon touchdown, Odysseus immediately began transmitting information back to Earth, the beginning of an extensive exploration mission.
Equipped with a suite of advanced sensors and scientific instruments, including cameras to examine changes in the lunar surface caused by spacecraft engine plumes and devices to analyze charged dust particle clouds formed by solar radiation during twilight, Odysseus is to unlock new insights into the moon’s geology and environment.
One of the features of Odysseus is its NASA landing device, which utilizes laser pulses to precisely measure frequency changes and signal return times, enabling the spacecraft to determine its velocity and distance from the lunar surface with unparalleled accuracy.
Odysseus carries payloads from various private companies and groups, underlining the collaborative nature of modern space exploration.
From cameras designed by students and faculty at Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University to an art installation commemorating human curiosity.
Also Read: UK Nuclear fusion Reactor Set New World Record for Energy Output























