Scientists have discovered a colossal volcano on Mars, challenging our understanding of the Red Planet’s geological history and offering prospects for future exploration. The discovery announced at the 55th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference in Texas.

Also Read: New Zealand: Scientists Discovered 100 New Marine Species
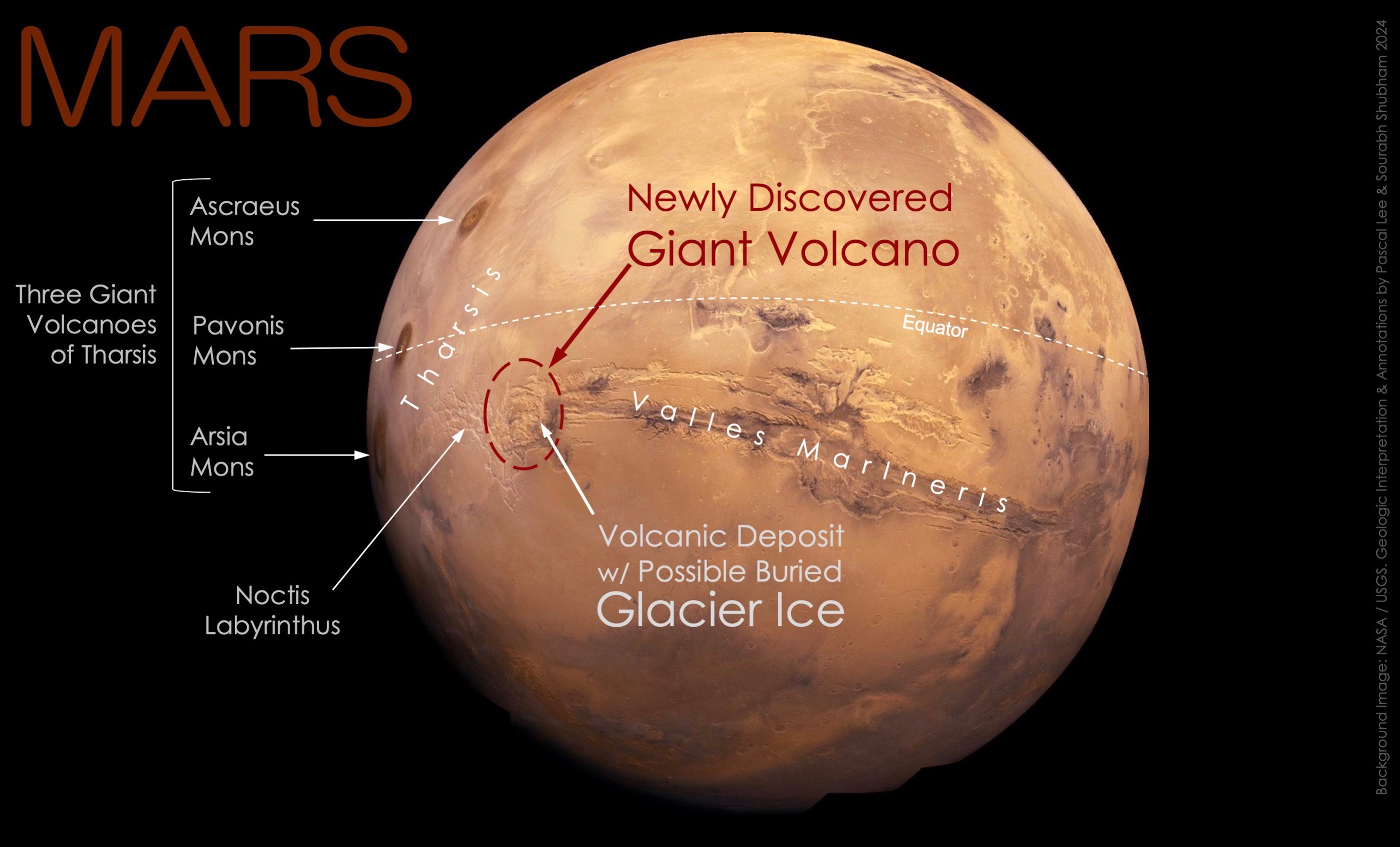
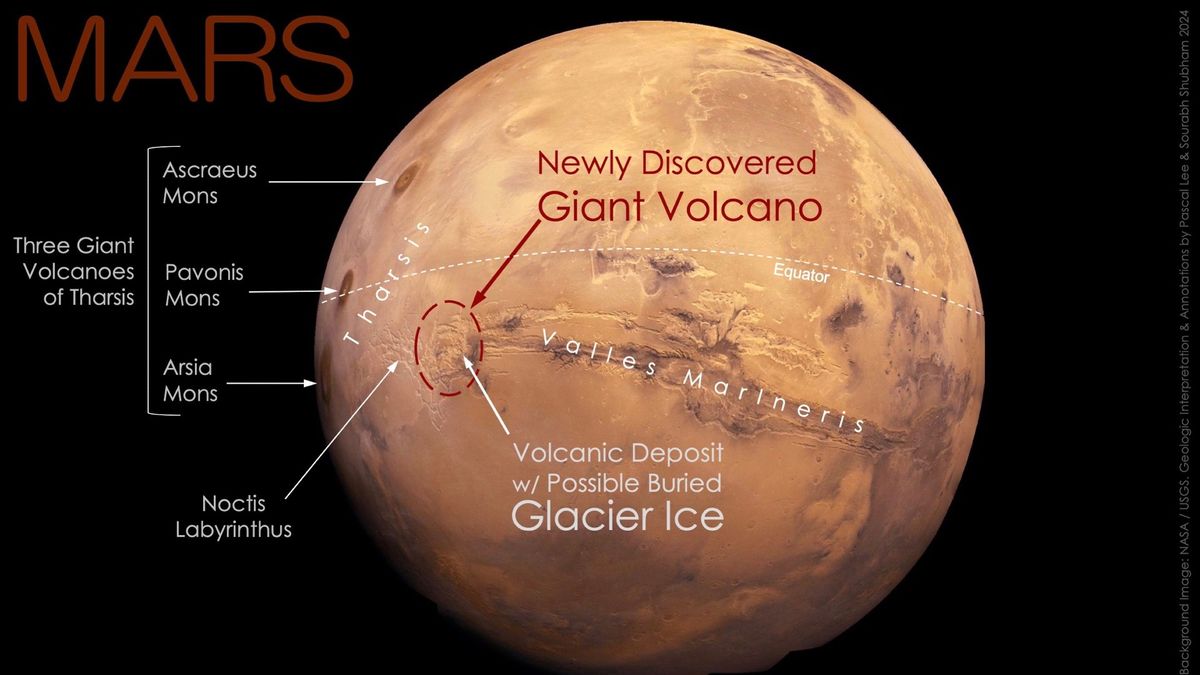
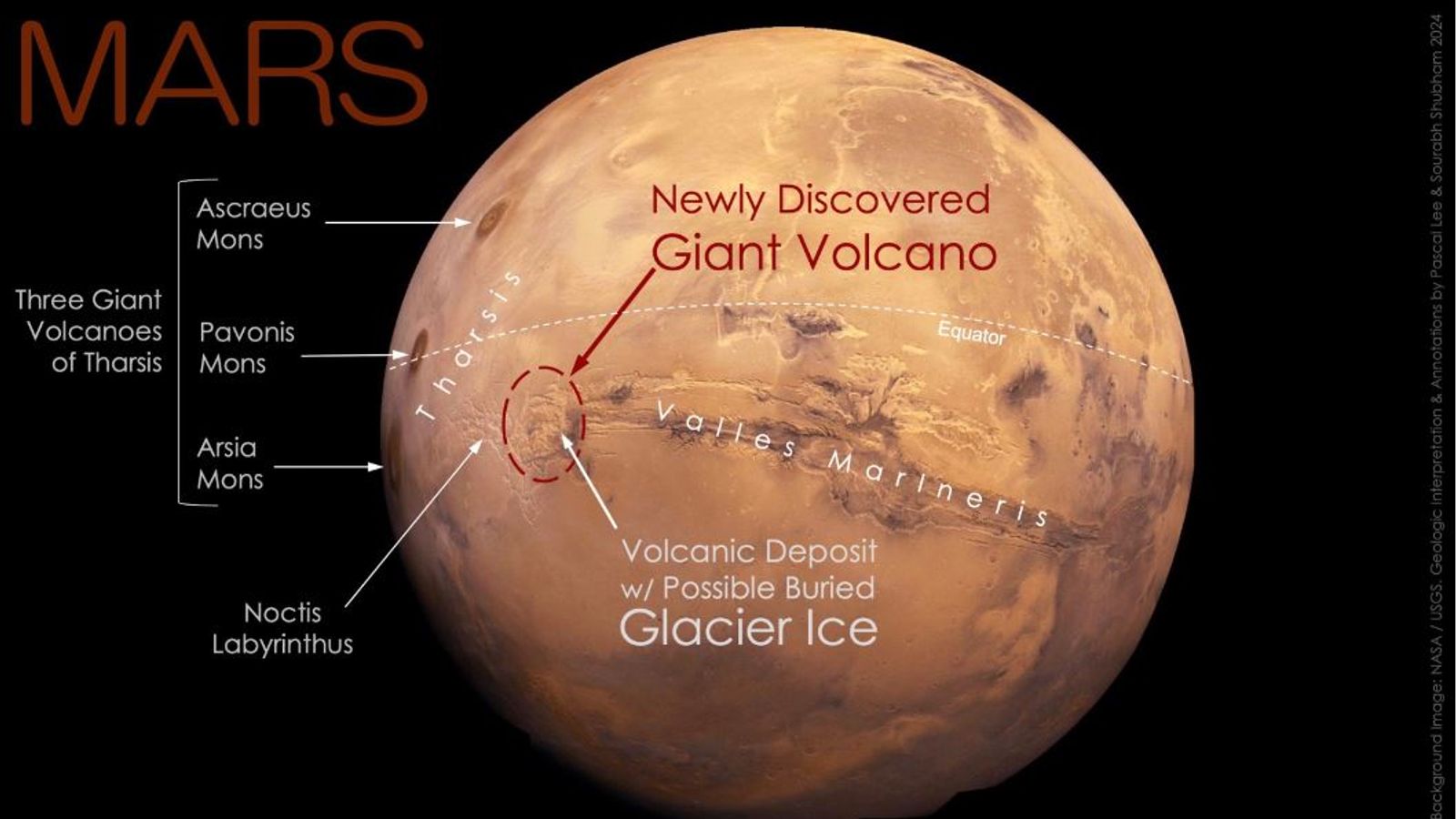
The newly discovered volcano measuring a 280 miles in width and towering over 29,600 feet in elevation, has long detection despite being captured in numerous images by spacecraft orbiting Mars since 1971.
Situated at the boundary of the Noctis Labyrinthus and the Valles Marineris, Noctis Mons represents an addition to Mars’ volcanic landscape.
Nestled in the eastern part of Mars’ Tharsis volcanic region, the Noctis Volcano spans an 280 miles in width, towering over the Martian landscape at a elevation of 9,022 meters.
Despite its size, this geological behemoth remained concealed for decades, camouflaged amidst the terrain of the planet’s surface.
The size and complex history of Noctis Mons suggest volcanic activity potentially spanning ancient through recent times.
A thin layer of volcanic deposit covering the southeastern part of the volcano hints at ongoing geological processes beneath its surface.
The revelation of the Noctis Volcano stems from analysis of data collected by various orbiting spacecraft including NASA’s Mariner 9, Viking Orbiter 1 and 2, Mars Global Surveyor, Mars Odyssey, and Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter missions, alongside ESA’s Mars Express mission.
This collaborative effort underlines the interdisciplinary nature of modern planetary science, where data from diverse sources converge to reveal the secrets of distant worlds.
Detailed observations reveal a myriad of geological features within the Noctis Volcano’s vicinity, including a caldera remnant, lava flows, and pyroclastic deposits.
Also Read: Odysseus Completes First US Moon Landing Since 1972
The presence of hydrated mineral deposits hints at Mars’ past characterized by volcanic activity and water interactions.
The identification of “rootless cones” within the volcanic perimeter shows explosive steam venting indicative of volatile interactions beneath the Martian surface.
Adjacent to Noctis Mons lies a buried glacier ice sheet offering tantalizing prospects for Martian exploration.
This discovery corroborates previous findings of surface water ice on Mars, indicating the presence of subsurface water reservoirs. The coexistence of a massive volcano and glacier ice unveils a rich tapestry of Martian geology.
The combined discovery of Noctis Mons and the buried glacier ice opens new avenues for studying Mars’ geologic evolution and searching for signs of life.
The presence of water ice near the equator holds promise for future human missions, providing a resource for hydration and fuel production.
The unveiling of Noctis Mons and the buried glacier ice represents a culmination of collaborative research efforts between the SETI Institute, the Mars Institute, and NASA’s Ames Research Center.
The unveiling of the Noctis Volcano is the culmination of analysis of data collected by an array of orbiting spacecraft, including NASA’s Mariner 9, Viking Orbiter 1 and 2, Mars Global Surveyor, Mars Odyssey, and Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter missions, alongside ESA’s Mars Express mission.
Detailed observations of the Noctis Volcano reveal a plethora of geological features including a caldera remnant, extensive lava flows, and pyroclastic deposits.
The presence of hydrated mineral deposits hints at Mars’ geological history characterized by volcanic activity and interactions with water.
Also Read: Neuralink’s First Human Patient able to Control Mouse through Thinking