Elon Musk’s SpaceX successfully launched its first set of Starlink satellites designed to provide global cell phone service. The initiative is to address cellular dead zones and enhance mobile connectivity across the world.

Also Read: North Korea to Launch 3 More Spy Satellites in 2024
This announced on January 3, 2024, is a step in Elon Musk’s plan to create a satellite constellation with the goal of offering high-speed internet access to every corner of the Earth.
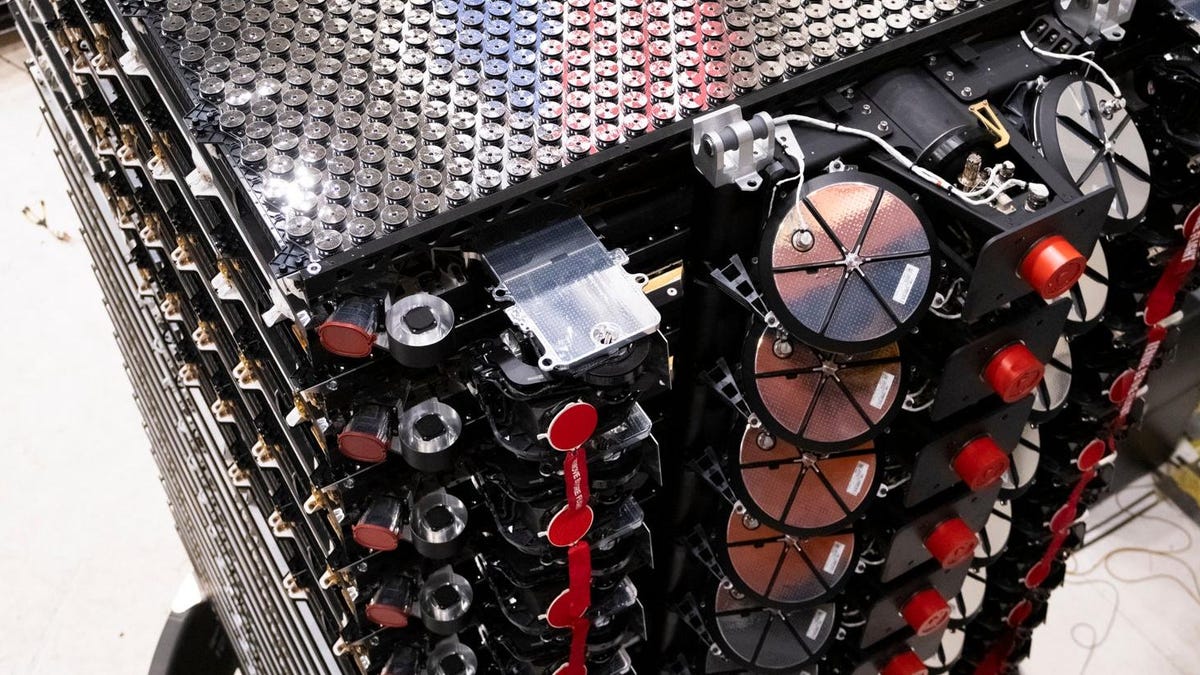
The launch included 21 Starlink satellites, with six of them equipped for direct connection to cell phones, making SpaceX’s first-ever direct-to-cell satellites.
These satellites function as cellphone towers in space, according to Starlink‘s official website, aiming to eliminate signal dead zones and provide seamless mobile connectivity.
The advanced eNodeB modem onboard enables direct communication with cell phones, without the need for additional equipment.
SpaceX plans to initially test its Direct-to-Cell service in the United States, where the company has partnered with T-Mobile.
The service is designed to connect with ordinary 4G LTE-compatible phones without requiring any additional hardware.
Also Read: U.S Military Launches X-37B Robot Space Plane for 7th Secretive Mission
T-Mobile, in collaboration with SpaceX, is to leverage the existing 4G LTE standard, covering a majority of smartphones on its network since 2022.
Elon Musk acknowledged the technology’s limitations, stating that while it is a great solution for areas without cellular connectivity, it is not competitive with existing terrestrial cellular networks due to limited bandwidth spread over large areas.
Starlink plans to introduce a text messaging service using this technology later in the year, with broader voice, data, and IoT services by 2025.
Starlink envisions extending its Direct-to-Cell service globally, partnering with carriers worldwide. The existing partnerships with carriers such as Optus in Australia, Rogers in Canada, KDDI in Japan, Salt in Switzerland, and Entel in Chile and Peru.
The rollout timeline and specific details about connectivity at home and abroad remain unclear. The Direct-to-Cell technology utilizes LTE phones, acting as a cell phone tower in space.
This eliminates the need for an intermediate ground-based infrastructure, enabling direct communication between satellites and individual cellular devices.
Also Read: China’s Ocean Drilling Ship Mengxiang to be First to Reach Earth’s Mantle
Starlink addresses that the service will be available in remote regions and partner countries, ensuring access to texting, calling, and browsing.
Elon Musk addressed that the Direct-to-Cell capability supports 7 MB per beam, making it suitable for areas lacking cellular connectivity.
The large beams are designed to cover expansive areas, contributing to the elimination of dead zones. The global impact of these satellites is expected to enhance connectivity and provide access in remote and rural areas.
With a vision to deploy a constellation of 42,000 satellites, Starlink aims to offer high-speed internet service globally.
SpaceX continues to advance its position in satellite internet, with over 5,000 active satellites providing relatively low-latency internet from orbit.
Elon Musk’s diverse portfolio, including Tesla, SpaceX, Neuralink, and the Boring Company, contributes to his estimated net worth of $251.3 billion.
Also Read: HD110067: Astronomers Discover Six-Planet Solar System





/cloudfront-us-east-2.images.arcpublishing.com/reuters/73PVHSXKT5LIHDTFDWHUSDQTL4.jpg)
















