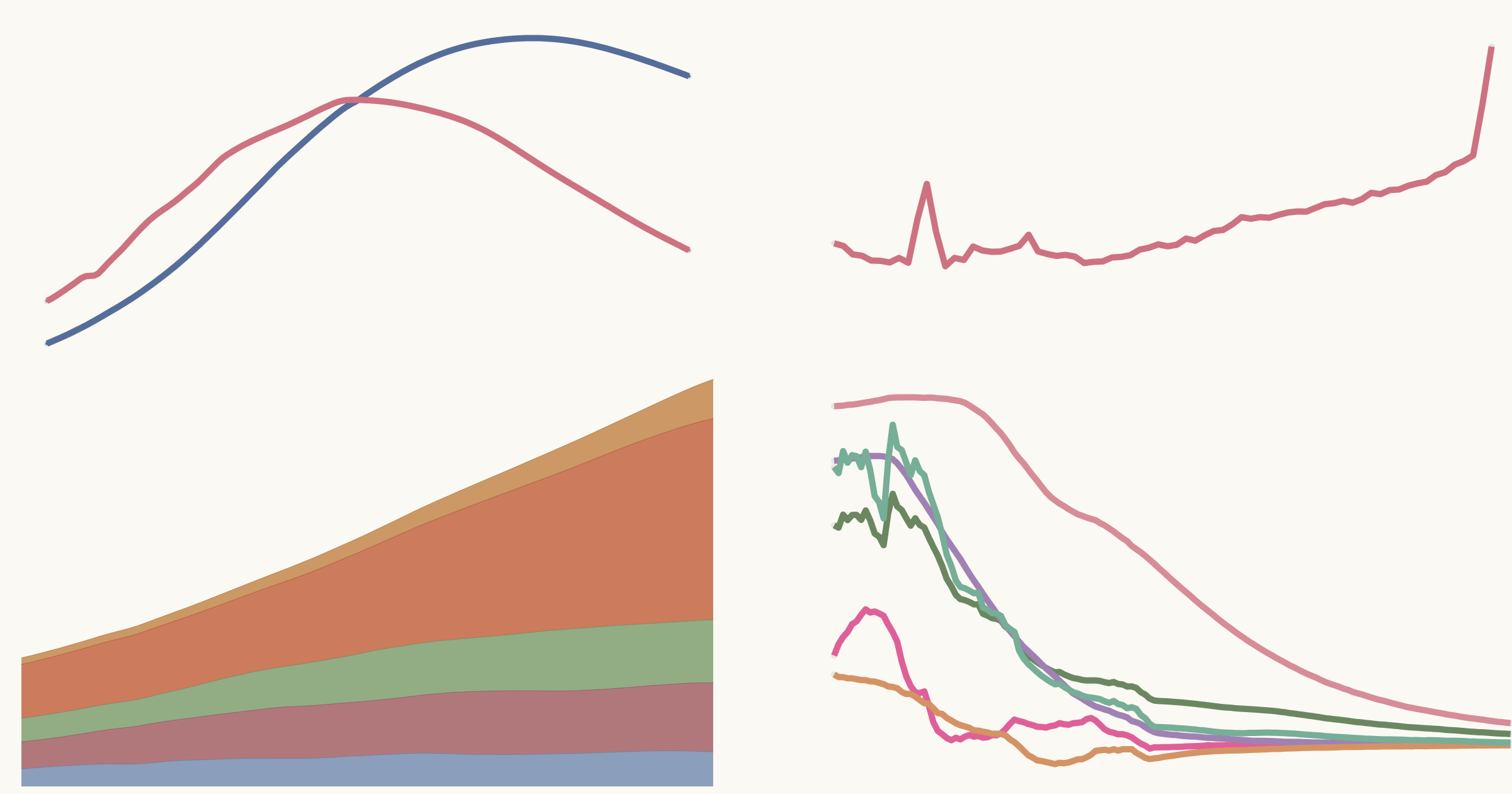
The United Nations (UN) projects that the world population will peak in the mid-2080s reaching approximately 10.3 billion people. The population is expected to gradually decline reaching about 10.2 billion by the end of the century. The current global population in 2024 stands at 8.2 billion.

Also Read: China: Man Caught Smuggling Over 100 Live Snakes Hidden in Pants
The projections indicate a 6% lower peak world population compared to estimates made a decade ago. This translates to 700 million fewer people than previously anticipated.
Factors contributing to this revision include lower fertility rates and faster declines in high-fertility regions.
Women globally are having one child fewer on average compared to 1990. Over half of all countries now have fertility rates below 2.1 live births per woman, the level required for a population to maintain its size without migration.
Countries such as China, Italy, the Republic of Korea and Spain exhibit ultra-low fertility rates with fewer than 1.4 live births per woman.
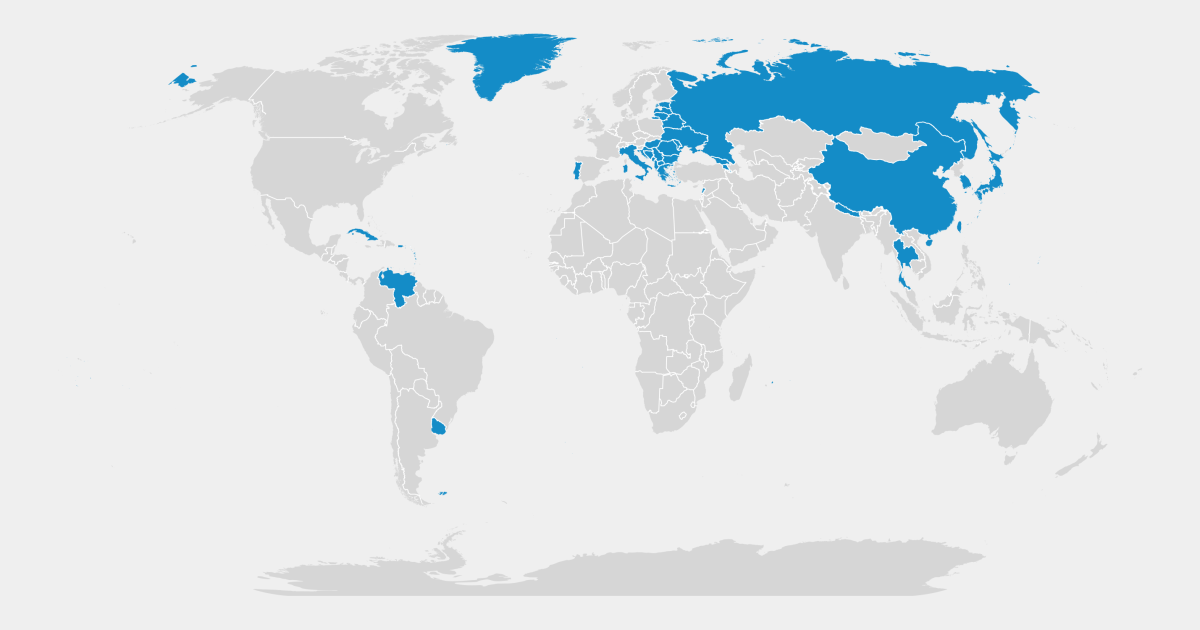
As of 2024, 63 countries including China, Germany, Japan and the Russian Federation have peaked.
These countries are expected to see a 14% decline over the next 30 years. An additional 48 countries including Brazil, Iran, Türkiye and Viet Nam are projected to peak between 2025 and 2054.
In 126 countries including India, Indonesia, Nigeria, Pakistan, and the USA populations are expected to grow until at least 2054.
Some countries such as Angola, the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Niger and Somalia are projected to see very rapid growth.
Early pregnancies remain a issue in low-income countries. In 2024, about 4.7 million babies (3.5% of total global births) were born to mothers under age 18.
Approximately 340,000 were born to children under age 15 having serious health risks for both mothers and children.
Mortality rates have decreased and life expectancy has increased over the past three decades. Global life expectancy at birth is rising, reaching 73.3 years in 2024, up from 70.9 years during the COVID-19 pandemic. By the late 2050s over half of all global deaths will occur at age 80 or higher.
By the late 2070s the number of people aged 65 years or older is projected to surpass the number of children under 18.
By the mid-2030s individuals aged 80 and above are expected to outnumber infants under age 1. Even in rapidly growing youth, the number of people aged 65 or older is expected to rise over the next 30 years.
Also Read: China’s Cooking Oil Scandal Revives Food Safety Crisis
Investing in the education of young people, especially girls and increasing the age of marriage and first childbirth are crucial.
These measures can have positive outcomes for women’s health, educational attainment and labor force participation.
Slowing population growth through these investments can reduce the scale of required investments to achieve sustainable development.
India is projected to peak in the early 2060s at around 1.7 billion. After the peak, India is expected to decline by 12%, but it will remain the world’s most populous nation throughout the century. By 2100, India’s population is projected to be around 1.5 billion.
China is currently at 1.41 billion and is expected to fall to 1.21 billion by 2054 and further decline to 633 million by 2100.
On average, women worldwide are having one child fewer than they did around 1990. In more than half of all countries, the average number of live births per woman is below 2.1, the level required for a population to maintain its size without migration.
Nearly a fifth of all countries including China, Italy, South Korea, and Spain, have fertility rates below 1.4 live births per woman, categorizing them as having “ultra-low” fertility.
As of 2024, populations have peaked in 63 countries including China, Germany, Japan, and Russia. These countries are projected to see a combined population decline of 14% over the next 30 years.
Another 48 countries, including Brazil, Iran, Turkey, and Vietnam, are expected to reach their peaks between 2025 and 2054.
In the remaining 126 countries including India, Indonesia, Nigeria, Pakistan, and the USA, populations are expected to grow until at least 2054.
In nine countries, including Angola, the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Niger, and Somalia populations are projected to double between 2024 and 2054.
India is currently 1.45 billion and is expected to peak at 1.7 billion around 2060. Following this peak, a decline of 12% is anticipate, bringing the population down to approximately 1.5 billion by 2100.
India recently surpassed China as the world’s most populous country and it is projected to maintain this status throughout the century.
China is expected to decline dropping from 1.41 billion to 1.21 billion by 2054 and further to 633 million by 2100.
Also Read: Google to Offer Free Dark Web Monitoring Service for All Users