Scientists have discovered a process of oxygen production occurring at the bottom of the Pacific Ocean that does not involve photosynthesis or living organisms. This finding was made in the depths of the Clarion-Clipperton Zone (CCZ) between Hawaii and Mexico.

Also Read: Scientists Design New Spacesuit that Can Turn Urine into Drinking Water
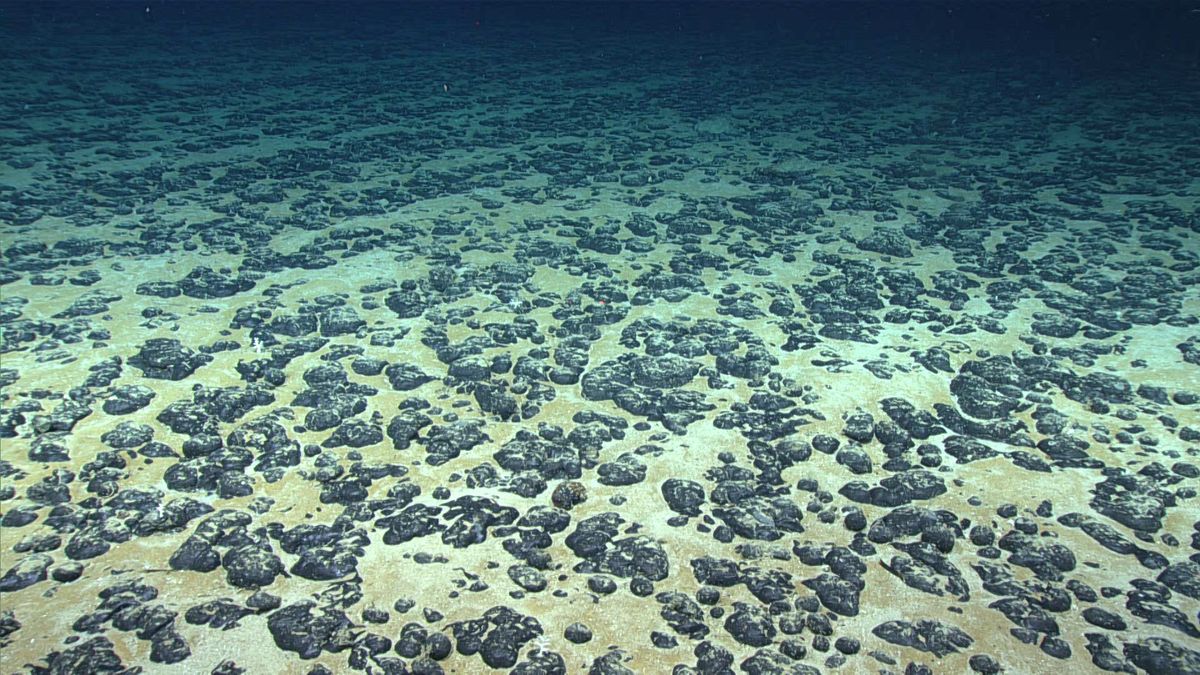
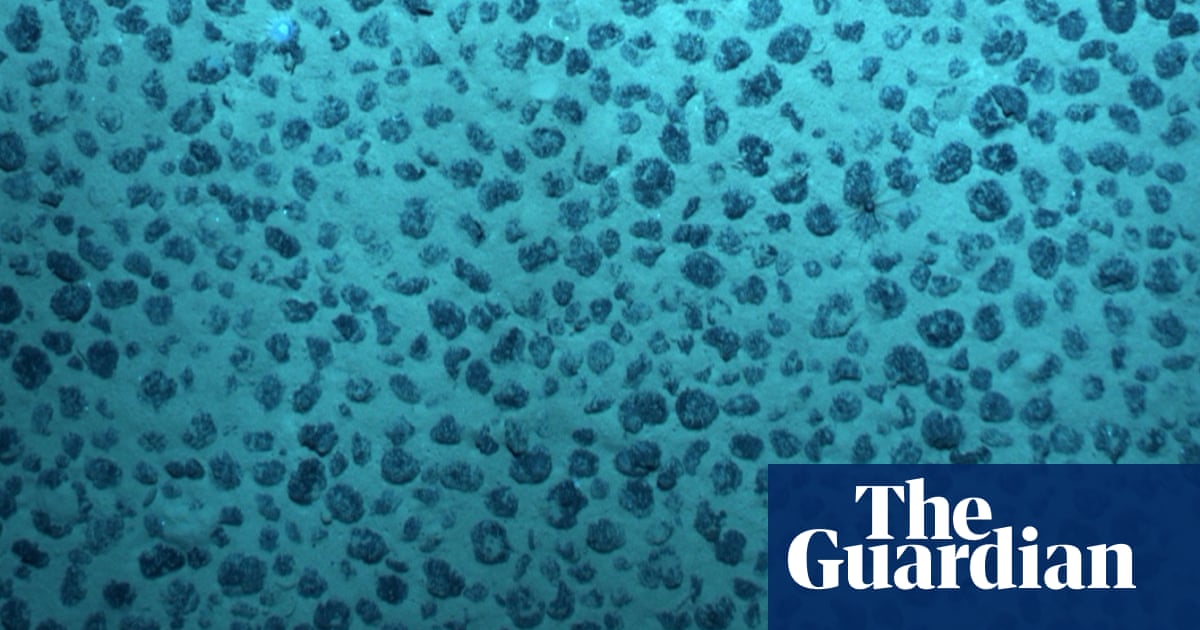
Researchers have identified that potato-sized metallic nodules on the ocean floor are capable of producing oxygen in complete darkness, a phenomenon now referred to as dark oxygen.
This contradicts the established understanding that oxygen is primarily produced by photosynthesis in plants, algae and cyanobacteria using sunlight.
These nodules are often described as batteries in a rock which are composed of oxides of iron and manganese and contain valuable metals such as cobalt, nickel, copper and rare earth elements.
They are abundant on the abyssal plains of the ocean floor at depths ranging from 3,000 to 6,000 meters (10,000 to 20,000 feet).
The nodules exhibit an electrical charge with voltages reaching almost as high as those found in AA batteries.
This electric is sufficient to split water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen in a process known as seawater electrolysis. This process does not rely on sunlight.
The research was led by Andrew Sweetman, a professor at the Scottish Association for Marine Science (SAMS). The study began with an expedition to the Clarion-Clipperton Zone, where the team aimed to understand the impact of deep-sea mining on the local ecosystem.
The team used a benthic chamber to isolate sections of the seafloor and measure oxygen levels. Oxygen levels in such chambers decrease over time as organisms consume the gas.
However, in this case oxygen levels increased, a result that initially baffled researchers and led them to suspect equipment malfunctions.
The experiments were conducted over multiple expeditions from 2013 to 2022. The consistency of the results across these years confirmed that the oxygen production was not an anomaly.
The team brought samples of the nodules to their ship’s laboratory and recreated the seafloor conditions. Again, they observed an increase in oxygen levels.
The vast expanse of the ocean has always been a subject of mystery. While sunlight-driven photosynthesis is the primary source of oxygen production on Earth, this research conducted in the Clarion-Clipperton Zone has unveiled an unexpected source of oxygen.
This discovery challenges the belief that oxygen production is exclusively linked to sunlight.
The journey to this discovery began in 2013 when Sweetman and his team observed unusual sensor readings aboard a research vessel.
Also Read: Fossil Chromosomes from Woolly Mammoth Discovered in 52,000-Year-Old Freeze Dried Skin
The readings showed oxygen production at the seafloor, 4,000 meters below the ocean surface where light is absent.
After years of observations and experiments, Sweetman and his colleagues proposed a hypothesis to explain dark oxygen production, the geobattery effect.
This theory suggests that metallic nodules found on the seafloor act like natural batteries generating electric currents that split seawater into oxygen and hydrogen through electrolysis.
Rich in metals like manganese, cobalt, nickel and copper. Nodules generate electric currents causing seawater electrolysis.
Nodules produce voltages of approximately 0.95 volts enough to trigger electrolysis when clustered together.
The deep-sea environment is home to a wide array of life forms, many of which rely on oxygen for survival.
Dark Oxygen production in the deep sea may support unique marine life forms. Potential to discover new species and ecosystems.
Mining could disrupt oxygen production and harm marine life. International Seabed Authority’s role in regulating mining activities. Scientists and environmentalists advocate for a moratorium on mining until research is conducted.
The concept of geobatteries and dark oxygen production offers possibilities for understanding the origins of life on Earth and the potential for life on other planets.
Deep-sea hydrothermal vents as sites for the evolution of life. Geobatteries may create oxygen-rich environments on other celestial bodies.
The emergence of oxygen and complex life on Earth is linked to the activity of ancient microbes known as cyanobacteria, which began producing oxygen through photosynthesis around 3 billion years ago.
This discovery suggests that oxygen could have been produced independently of biological processes.
If similar processes occur on other celestial bodies such as Jupiter’s moon Europa or Saturn’s moon Enceladus which are believed to have subsurface oceans, it could mean that oxygen-rich environments capable of supporting life might exist elsewhere in the solar system.
Also Read: Night Owls have Better Cognitive Ability than Early Risers